1. In thin freely suspended films of ferroelectric
and smectic C liquid crystals we have observed structures possessing
longitudinal polarization (parallel
to the tilt plane of the molecules). It was found that the temperature of the
transition from the state with transverse polarization into the state with
longitudinal polarization
increases wiht decreasing film
thickness. A model has been proposed relating the existence of longitudinal
polarization witn nonuniform
profile of the order parameter in the film which enables to calculate the
temperature dependence of the longitudinal polarization and transition
temperatures.
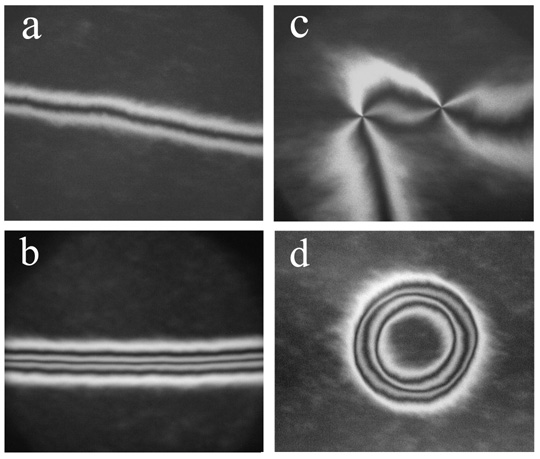
2. For the first time 2π- and π-walls were observed in thin freely
suspended films of nonpolar smectic liquid crystals (Fig.1). We have observed the dissotiation of
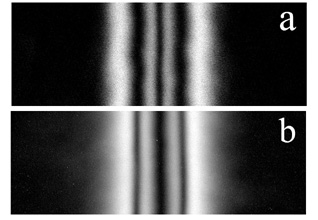
2π-walls on two π-walls upon changing the orientation of the magnetic field
with respect to the film plane (Fig.2) and dependence of the wall structure on orientation of
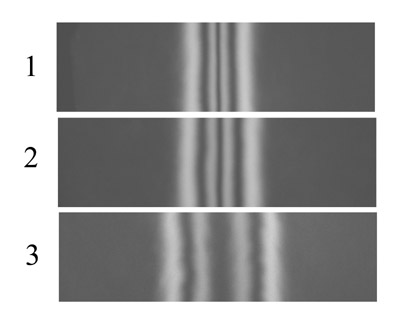
the wall with respect to the field direction (Fig.3).
Values of the two-dimensional orienational elastic constants were determined in antiferroelectric films, in smectic C and the value of longitudinal
electric polarization in antiferroelectric films.